A Decade of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Geography: Bibliometric Insights with AI-Powered Analysis
Published 2025-11-24
Keywords
- artificial intelligence (AI),
- geography,
- geoai,
- bibliometric insights,
- AI-powered analysis
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2025 Burak Oğlakcı , Alper Uzun

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2025-11-20
Published 2025-11-24
Abstract
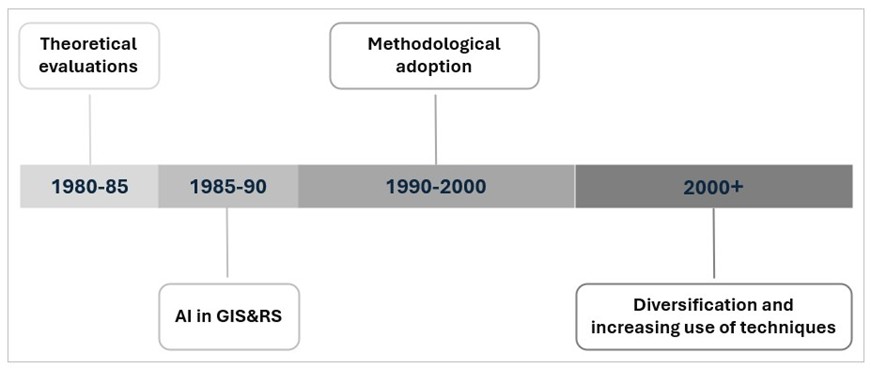
In the last decade, there has been a significant increase in the number of geography studies utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) applications and algorithms. Despite this increase, what is known about related studies is limited. The study aims to reveal the current state, trends, themes, and collaborations of the studies carried out in the interaction of AI and geography in the last decade and to highlight the prospects of AI within geography. Accordingly, the study is based on the bibliometric data of geography studies that have AI applications and algorithms. In the analysis of the data, basic analyses were first conducted covering titles, abstracts, keywords, and so on. Topic modelling was performed using the BERTopic to identify the research themes. Additionally, natural language processing (NLP) tasks were utilized to enhance the efficiency of the analysis. Between 2015 and 2024, productivity in the interaction of geography and AI has shown a significant increase, with 124 different countries contributing to this productivity. This reflects a growing global interest in the field. With increasing interest and productivity, it has been concluded that the methodologies, data, and focal topics have evolved and diversified, while the number of collaborations has also increased. The role of AI in geography is expected to become even more prominent in the future, thanks to its advanced data processing capacity, real-time analysis capabilities, and complex spatial modelling skills. However, soon, some specific approaches and issues (ethical and technical) regarding the interaction between geography and artificial intelligence are noteworthy.
Highlights:
- AI and geography research expanded globally, with 124 countries contributing.
- AI has evolved and diversified geography research methods, data, and focal topics.
- The role of AI in geography is expected to become more prominent.
- Ethical and technical issues in geography-AI interaction require urgent attention.
Downloads
References
- Abdollahi, A., & Pradhan, B. (2021). Urban vegetation mapping from aerial imagery using explainable AI (XAI). Sensors, 21(14), 4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144738
- Akinboyewa, T., Li, Z., Ning, H., & Lessani, M. N. (2025). GIS copilot: Towards an autonomous GIS agent for spatial analysis. International Journal of Digital Earth, 18(1), 2497489. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2025.2497489
- Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959-975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
- Arrieta, A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., Garcia, S., Gil-Lopez, S., Molina, D., Benjamins, R., Chatila, R., & Herrera, F. (2020). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. In-formation Fusion, 58, 82–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
- Badariotti, D., Banos, A., & Laperrière, V. (2007). Towards an individual-based approach to modelling and simulating spatial patterns of a com-municable disease: the plague in Madagascar. Cybergeo-European Journal of Geography, https://doi.org/10.4000/cybergeo.9052
- Barbanente, A., Borri, D., Esposito, F., Leo, P., Maciocco, G., & Selicato, F. (1992). Automatically acquiring knowledge by digital maps in artificial intelligence planning techniques. In Theories and Methods of Spatio-Temporal Reasoning in Geographic Space: International Conference GIS—From Space to Territory: Theories and Methods of Spatio-Temporal Reasoning Pisa, Italy, September 21–23, 1992 Proceedings (pp. 379-401). Springer.
- Bathaee, Y. (2018). The artificial intelligence black box and the failure of intent and causation. Harvard Journal of Law & Technology, 31(2), 889-938.
- Behl, S., Rao, A., Aggarwal, S., Chadha, S., & Pannu, H. S. (2021). Twitter for disaster relief through sentiment analysis for COVID-19 and natural hazard crises. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 55, 102101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102101
- Black, W. R. (1995). Spatial interaction modeling using artificial neural networks. Journal of Transport Geography, 3(3), 159-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/0966-6923(95)00013-S
- Boutayeb, A., Lahsen-Cherif, I., & El Khadimi, A. (2025). When machine learning meets geospatial data: a comprehensive GeoAI review. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 18,13135-13191. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3568715
- Carabantes, M. (2020). Black-box artificial intelligence: an epistemological and critical analysis. AI&Soc 35, 309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-019-00888-w
- Civco, D. L. (1993). Artificial neural networks for land-cover classification and mapping. International Journal of Geographical Information Sci-ence, 7(2), 173-186. https://doi.org/10.1080/02693799308901949
- Chen, H., Jiang, W., Yang, Y., Man, X., & Tang, M. (2015). A bibliometric analysis of waste management research during the period 1997–2014. Scientometrics, 105(2), 1005–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1714-3
- Cheng, S., Zhang, J., Wang, G., Zhou, Z., Du, J., Wang, L., ... & Wang, J. (2024). Cartography and neural networks: A scientometric analysis based on CiteSpace. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 13(6), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13060178
- Christodoulou, S., Deligianni, A., Aslani, P., & Agathokleous, A. (2009). Risk-based asset management of water piping networks using neurofuzzy systems. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 33(2), 138-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2008.12.001
- Crevier, D. (1993). AI: The tumultuous history of the search for artificial intelligence. Basic Books.
- Couclelis, H. (1986). Artificial intelligence in geography: conjectures on the shape of things to come. The Professional Geographer, 38(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0033-0124.1986.00001.x
- Cowen, D. J. (1983). Commentaries on “Automated Geography”. Automated geography and the DIDS (Decision Information Display System) experiment. The Professional Geographer, 35(3), 339-340. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0033-0124.1983.00339.x
- Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency-DARPA. (2016). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). Report No. DARPA-BAA-16-53. https://research-vp.tau.ac.il/sites/resauth.tau.ac.il/files/DARPA-BAA-16-53_Explainable_Artificial_Intelligence.pdf
- Doherty, P., Guo, Q., & Alvarez, O. (2013). Expert versus machine: A comparison of two suitability models for emergency helicopter landing areas in Yosemite National Park. The Professional Geographer, 65(3), 466-481. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2012.697857
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
- Duan, Y., Edwards, J. S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of big data–evolution, challenges and re-search agenda. International Journal of Information Management, 48, 63-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.01.021
- Egger R., & Yu J (2022) A topic modeling comparison between LDA, NMF, Top2Vec, and BERTopic to demystify Twitter posts. Front. Sociol. 7:886498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoc.2022.886498
- Estes, J. E., Sailer, C., & Tinney, L. R. (1986). Applications of artificial intelligence techniques to remote sensing. The Professional Geographer, 38(2), 133–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0033-0124.1986.00133.x
- EuroGEO (2024). A review of AI and Ethics in Geography/geospatial education. GeoDem-AI Project.
- Fabricius, C., & Coetzee, K. (1992). Geographic information systems and artificial intelligence for predicting the presence or absence of mountain reedbuck. South African Journal of Wildlife Research-24-month delayed open access, 22(3), 80-86.
- Fisher, P. F. (1989). Expert system applications in geography. Area, 21(3), 279-287.
- Fisher, P. F., Mackaness, W. A., Peacegood, G., & Wilkinson, G. G. (1988). Artificial intelligence and expert systems in geodata processing. Progress in physical geography, 12(3), https://doi.org/10.1177/030913338801200303
- Frank, A. U., Hudson, D. L., & Robinson, V. B. (1987). Artificial intelligence tools for GIS. International Geographic Information Systems Symposium: the research agenda, November 15-18, 1987, Arlington, Virginia.
- Frankish, K., & Ramsey, W. M. (Eds.). (2014). The Cambridge handbook of artificial intelligence. Cambridge University Press.
- Franklin, S. (2014). History, motivations, and core themes. In K. Frankish & W. M. Ramsey (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of artificial intelligence, (pp. 15-33). Cambridge University Press.
- Gahegan, M. (2000). On the application of inductive machine learning tools to geographical analysis. Geographical Analysis, 32(2), 113-139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.2000.tb00420.x
- Gao, S., Hu, Y., & Li, W. (2023). Introduction to geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI). In Handbook of geospatial artificial intelligence (pp. 3-16). CRC Press.
- Griffin, A. L. (2020). Trustworthy maps. Journal of Spatial Information Science, 20(20), 5–19. https://doi.org/10.5311/ JOSIS.2020.20.654
- Grootendorst, M. (2022). BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.05794. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.05794
- Guo, Y., Barnes, S. J., and Jia, Q. (2017). Mining meaning from online ratings and reviews: tourist satisfaction analysis using latent dirichlet alloca-tion. Tour. Manag. 59, 467–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.09.009
- Guo, X., Hou, B., Ren, B., Ren, Z., & Jiao, L. (2021). Network pruning for remote sensing images classification based on interpretable CNNs. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 60, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3077062
- Hagenauer, J., & Helbich, M. (2012). Mining urban land-use patterns from volunteered geographic information by means of genetic algorithms and artificial neural networks. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 26(6), 963-982. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2011.619501
- Harzing, A. W., & Alakangas, S. (2016). Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: a longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scien-tometrics, 106, 787-804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1798-9
- Hashim, S., Omar, M. K., Ab Jalil, H., & Sharef, N. M. (2022). Trends on technologies and artificial intelligence in education for personalized learn-ing: systematic literature. Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 12(1), 884-903. http://dx.doi.org/10.6007/IJARPED/v11-i1/12230
- Huang, X., & Jensen, J. R. (1997). A machine-learning approach to automated knowledge-base building for remote sensing image analysis with GIS data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 63(10), 1185-1193.
- IGIS (1987). International Geographic Information Systems Symposium: the research agenda, November 15-18, 1987, Arlington, Virginia.
- Jachowski, N. R., Quak, M. S., Friess, D. A., Duangnamon, D., Webb, E. L., & Ziegler, A. D. (2013). Mangrove biomass estimation in Southwest Thailand using machine learning. Applied Geography, 45, 311-321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.09.024
- Janowicz, K., Gao, S., McKenzie, G., Hu, Y., & Bhaduri, B. (2020). GeoAI: spatially explicit artificial intelligence techniques for geographic knowledge discovery and beyond. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 34(4), 625-636. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2019.1684500
- Janowicz, K., Sieber, R., & Crampton, J. (2022). GeoAI, counter-AI, and human geography: A conversation. Dialogues in Human Geography, 12(3), 446-458. https://doi.org/10.1177/20438206221132510
- Janowicz, K., Liu, Z., Mai, G., Wang, Z., Majic, I., Fortacz, A., McKenzie, G., & Gao, S. (2025). Whose truth? Pluralistic geo-alignment for (agentic) AI. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2508.05432
- Jiang, S., Ma, J., Liu, Z., & Guo, H. (2022). Scientometric analysis of artificial intelligence (AI) for geohazard research. Sensors, 22(20), 7814. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207814
- Kahraman, M. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of slums. Turkish Research - Social, 17(6), 1151-1168. https://dx.doi.org/10.7827/TurkishResearch.64417
- Kang, S., He, L., Lin, Z., & Luo, W. (2025). GeoAI and Economic Geography. In GeoAI and Human Geography: The Dawn of a New Spatial Intelli-gence Era (pp. 147-162). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Kang, Y., Gao, S., & Roth, R. E. (2024). Artificial intelligence studies in cartography: a review and synthesis of methods, applications, and eth-ics. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 51(4), 599-630. https://doi.org/10.1080/15230406.2023.2295943
- Khanal, S., Zhang, H., & Taeihagh, A. (2024). Development of new generation of artificial intelligence in China: When Beijing’s global ambitions meet local realities. Journal of Contemporary China, 34(151), 19–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/10670564.2024.2333492
- Kraus, S., Bouncken, R. B., & Yela Aránega, A. (2024). The burgeoning role of literature review articles in management research: An introduction and outlook. Review of Managerial Science, 18(2), 299-314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-024-00729-1
- Laffan, S. W., Nielsen, O. M., Silcock, H., & Hegland, M. (2005). Sparse grids: A new predictive modelling method for the analysis of geographic data. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 19(3), 267–292. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810512331319118
- Lamovec, P., & Ostir, K. (2010). Application of data mining for determination of flooded areas: Selska Valley 2007 floods case study. Geodetski Vestnik, 54(4), 661–675. https://doi.org/10.15292/geodetski-vestnik.2010.04.661-675
- Lavallin, A., & Downs, J. A. (2021). Machine learning in geography: Past, present, and future. Geography Compass, 15(5), e12563. https://doi.org/10.1111/gec3.12563
- Lees, B. G., & Ritman, K. (1991). Decision-tree and rule-induction approach to integration of remotely sensed and GIS data in mapping vegeta-tion in disturbed or hilly environments. Environmental Management, 15(6), 823–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02394820
- Li, W., Arundel, S., Gao, S., Goodchild, M., Hu, Y., Wang, S., & Zipf, A. (2024). GeoAI for science and the science of GeoAI. Journal of Spatial Infor-mation Science, (29), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.5311/JOSIS.2024.29.349
- Li, W., & Hsu, C. Y. (2022). GeoAI for large-scale image analysis and machine vision: Recent progress of artificial intelligence in geography. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(7), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11070385
- Li, X., & Yeh, A. G. O. (2002). Neural-network-based cellular automata for simulating multiple land use changes using GIS. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 16(4), 323–343. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810210137004
- Li, Z. (2022). Extracting spatial effects from machine learning model using local interpretation method: An example of SHAP and XGBoost. Com-puters, Environment and Urban Systems, 96, 101845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2022.101845
- Li, Z., & Ning, H. (2023). Autonomous GIS: The next-generation AI-powered GIS. International Journal of Digital Earth, 16(2), 4668–4686. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2023.2278895
- Li, Z., Ning, H., Gao, S., Janowicz, K., Li, W., Arundel, S. T., … Hodgson, M. E. (2025). GIScience in the era of artificial intelligence: A research agen-da towards autonomous GIS. Annals of GIS, 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475683.2025.2552161
- Linnenluecke, M. K., Marrone, M., & Singh, A. K. (2020). Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Australian Journal of Management, 45(2), 175–194. https://doi.org/10.1177/0312896219877678
- Littman, M. L., Ajunwa, I., Berger, G., Boutilier, C., Currie, M., Doshi-Velez, F., ... Walsh, T. (2021). Gathering strength, gathering storms: The One Hundred Year Study on Artificial Intelligence (AI100) 2021 study panel report. Stanford University. http://ai100.stanford.edu/2021-report
- Liu, P., Hou, Y., Lei, B., Liang, X., & Biljecki, F. (2025). GeoAI and urban geography. In G. Mai, S. Gao, & K. Janowicz (Eds.), GeoAI and human geog-raphy: The dawn of a new spatial intelligence era (pp. 251–266). Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Liu, W., Gu, M., Hu, G., Li, C., Liao, H., Tang, L., & Shapira, P. (2014). Profile of developments in biomass-based bioenergy research: A 20-year perspective. Scientometrics, 99(Suppl. 1), 507–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-013-1152-z
- Liu, Z., Janowicz, K., Cai, L., Zhu, R., Mai, G., & Shi, M. (2022). Geoparsing: Solved or biased? An evaluation of geographic biases in geoparsing. AGILE: GIScience Series, 3, 9. https://doi.org/10.5194/agile-giss-3-9-2022
- Mai, G., Hu, Y., Gao, S., Cai, L., Martins, B., Scholz, J., Gao, J., & Janowicz, K. (2022). Symbolic and subsymbolic GeoAI: Geospatial knowledge graphs and spatially explicit machine learning. Transactions in GIS, 26(8), 3118-3124. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.13012
- Mai, G., Xie, Y., Jia, X., Lao, N., Rao, J., Zhu, Q., ... & Jiao, J. (2025). Towards the next generation of geospatial artificial intelligence. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 136, 104368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2025.104368
- Manvi, R., Khanna, S., Burke, M., Lobell, D., & Ermon, S. (2024). Large language models are geographically biased. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.02680. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.02680
- Mao, H.; Hu, Y.; Kar, B.; Gao, S.; McKenzie, G. (2017). GeoAI 2017 Workshop Report: The 1st ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on GeoAI: AI and Deep Learning for Geographic Knowledge Discovery. Redondo Beach, CA, USA-November 7, 2016. ACM Sigspatial Spec., 9, 25
- McCarthy, J. (2007). What is Artificial Intelligence? http://jmc.stanford.edu/articles/whatisai.html
- McKeown, D.M. (1987). The role of artificial intelligence in the integration of remotely sensed data with geographic information systems. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, GE-25, 330-348. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.1987.289804
- Naderi, J. R., & Raman, B. (2005). Capturing impressions of pedestrian landscapes used for healing purposes with decision tree learn-ing. Landscape and Urban Planning, 73(2-3), 155-166. https://doi.org/10.1177/193758670800200112
- Nilsson, N. J. (2010). The quest for artificial intelligence: A history of ideas and achievements. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511819346
- Ninkov, A., Frank, J. R., & Maggio, L. A. (2022). Bibliometrics: methods for studying academic publishing. Perspectives on Medical Education, 11(3), 173-176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-021-00695-4
- Nystuen, J. D. (1984). Comment on “Artificial intelligence and its applicability to geographical problem solving”. The Professional Geogra-pher, 36(3), 358-359. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781784717544.00031
- Openshaw S. & Wymer C. (1991). A neural net classifier for handling census data. In Murtagh F. (Ed.), Neural networks for statistical and economic data. Munotec Systems.
- Openshaw, S. (1992). Some suggestions concerning the development of artificial intelligence tools for spatial modelling and analysis in GIS. The Annals of Regional Science, 26, 35-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581479
- Openshaw, S. (1995). Developing automated and smart spatial pattern exploration tools for geographical information systems applica-tions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series D (The Statistician), 44(1), 3-16. https://doi.org/10.2307/2348611
- Openshaw, S., & Openshaw, C. (1997). Artificial Intelligence in Geography. Wiley.
- Özgen, N. (2010). Bilim olarak coğrafya ve evrimsel paradigmaları. Ege Coğrafya Dergisi, 19(2), 1-26.
- Papadimitriou, F. (2025). The rise of spatial AI. In Spatial Artificial Intelligence (Springer Briefs in Applied Sciences and Technology). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-82136-3_1
- Pereira, V., Basilio, M. P., & Santos, C. H. T. (2025). PyBibX–a Python library for bibliometric and scientometric analysis powered with artificial intelligence tools. Data Technologies and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1108/DTA-08-2023-0461
- Pessin, V. Z., Yamane, L. H., & Siman, R. R. (2022). Smart bibliometrics: an integrated method of science mapping and bibliometric analy-sis. Scientometrics, 127(6), 3695-3718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-022-04406-6
- Pijanowski, B. C., Pithadia, S., Shellito, B. A., & Alexandridis, K. (2005). Calibrating a neural network‐based urban change model for two metropol-itan areas of the Upper Midwest of the United States. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 19(2), 197-215. doi:10.1080/13658810410001713416
- Rai, A. (2020). Explainable AI: From black box to glass box. Journal of The Academy of Marketing Science, 48(1), 137-141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-00710-5
- Ramaswamy, V. V., Lin, S. Y., Zhao, D., Adcock, A., van der Maaten, L., Ghadiyaram, D., & Russakovsky, O. (2023). Geode: a geographically diverse evaluation dataset for object recognition. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36, 66127-66137. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.02560
- Rienow, A., & Stenger, D. (2014). Geosimulation of urban growth and demographic decline in the Ruhr: a case study for 2025 using the artificial intelligence of cells and agents. Journal of Geographical Systems, 16, 311-342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10109-014-0196-9
- Rigol, J. P., Jarvis, C. H., & Stuart, N. (2001). Artificial neural networks as a tool for spatial interpolation. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 15(4), 323-343. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810110038951
- Ritter, N. D., & Hepner, G. F. (1990). Application of an artificial neural network to land-cover classification of thematic mapper image-ry. Computers & Geosciences, 16(6), 873-880.
- Robinson, V. B., & Lundberg, C. G. (1987). Organizational and knowledge base considerations for the design of distributed geographic infor-mation systems lessons from semantic modeling. International Geographic Information Systems Symposium: the research agenda, Novem-ber 15-18, 1987, Arlington, Virginia.
- Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial intelligence: A modern approach (3rd ed.). Pearson.
- Say, C. (2021). 50 Soruda Yapay Zekâ. (21st Edition). Bilim ve Gelecek Yayınevi.
- Se, K. (2024). What is Spatial Intelligence? TuringPost. https://www.turingpost.com/p/cvhistory5
- Shi, M., Janowicz, K., Verstegen, J., Currier, K., Wiedemann, N., Mai, G., ... & Zhu, R. (2025). Geography for AI sustainability and sustainability for GeoAI. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 52(4), 331-349.
- Siau, K., & Wang, W. (2020). Artificial intelligence (AI) ethics: Ethics of AI and ethical AI. Journal of Database Management, 31(2), 74–87. https://doi.org/10.4018/JDM. 2020040105
- Smith, T. R. (1984). Artificial intelligence and its applicability to geographical problem solving. The Professional Geographer, 36(2), 147-158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0033-0124.1984.00147.x
- Song, Y., Kalacska, M., Gašparović, M., Yao, J., & Najibi, N. (2023). Advances in geocomputation and geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI) for mapping. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 120, 103300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2023.103300
- Steiniger, S., Taillandier, P., & Weibel, R. (2010). Utilising urban context recognition and machine learning to improve the generalisation of build-ings. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24(2), 253-282. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810902798099
- Stone, P., Brooks, R., Brynjolfsson, E., Calo, R., Etzioni, O., Hager, G., Hirschberg, J., Kalyanakrishnan, S., Kamar, E., Kraus, S., Leyton-Brown, K., Parkes, D., Press, W., Saxenian, A., Shah, J., Tambe, M., & Teller, A. (2016). Artificial Intelligence and Life in 2030. One Hundred Year Study on Artificial Intelligence: Report of the 2015-2016 Study Panel, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, ai100.stanford.edu/2016-report
- Tanrıkulu, M., & Gümüşçü, O. (2021). Türkiye’de coğrafya biliminin gelişimi: 1940-2000 dönemi. Türkiye Araştırmaları Literatür Dergisi, 19(37), 467-512.
- Tikunov, V. S. (1990). Research on artificial intelligence and expert systems in geography. Soviet Geography, 31(2), 126–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/00385417.1990.10640821
- Turing, A. (1950). Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind, 59(236), 433-460. https://doi.org/10.1093/mind/LIX.236.433
- Uysal, M., Topal M., & Kaymak, Z. D. (2024). Artificial intelligence and education: An insight through bibliometric analysis. Van Yüzüncü Yıl Üniver-sitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 21(2), 450-470. https://doi.org/10.33711/yyuefd.1381074
- VoPham, T., Hart, J. E., Laden, F., & Chiang, Y. Y. (2018). Emerging trends in geospatial artificial intelligence (geoAI): potential applications for environmental epidemiology. Environmental Health, 17(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0386-x
- Walker, M., & Winders, J. (2025). GeoAI and Political Geography. In GeoAI and Human Geography: The Dawn of a New Spatial Intelligence Era (pp. 181-191). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Wan, S., Lei, T. C., & Chou, T. Y. (2012). A landslide expert system: image classification through integration of data mining approaches for multi-category analysis. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 26(4), 747-770. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2011.613397
- Wang, S., Huang, X., Liu, P., Zhang, M., Biljecki, F., Hu, T., ... & Bao, S. (2024). Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial intelli-gence (GeoAI) in quantitative human geography: An extensive systematic review. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 128, 103734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2024.103734
- Whitby, B. (2012). Artificial intelligence a beginner’s guide. E-book Edition. Oneworld Publications.
- Xing, J., & Sieber, R. (2023). The challenges of integrating explainable artificial intelligence into GeoAI. Transactions in GIS, 27(3), 626-645.
- https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.13045
- Yılmaz, H. (2024). Biyolojik çeşitlilik muhasebesinin bibliyometrik analizi, Uluslararası Sosyal ve Ekonomik Çalışmalar Dergisi, 5(2), 337-360 https://doi.org/10.62001/gsijses.1554115
- Zhao, L., Tang, Z. Y., & Zou, X. (2019). Mapping the knowledge domain of smart-city research: A bibliometric and scientometric analy-sis. Sustainability, 11(23), 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236648
- Zhao, B., Zhang, S., Xu, C., Sun, Y., & Deng, C. (2021). Deep fake geography? When geospatial data encounter artificial intelligence. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 48(4), 338–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/15230406. 2021.1910075
- Zhou, F., Wang, T., Zhong, T., & Trajcevski, G. (2022). Identifying user geolocation with hierarchical graph neural networks and explainable fu-sion. Information Fusion, 81, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.11.004




