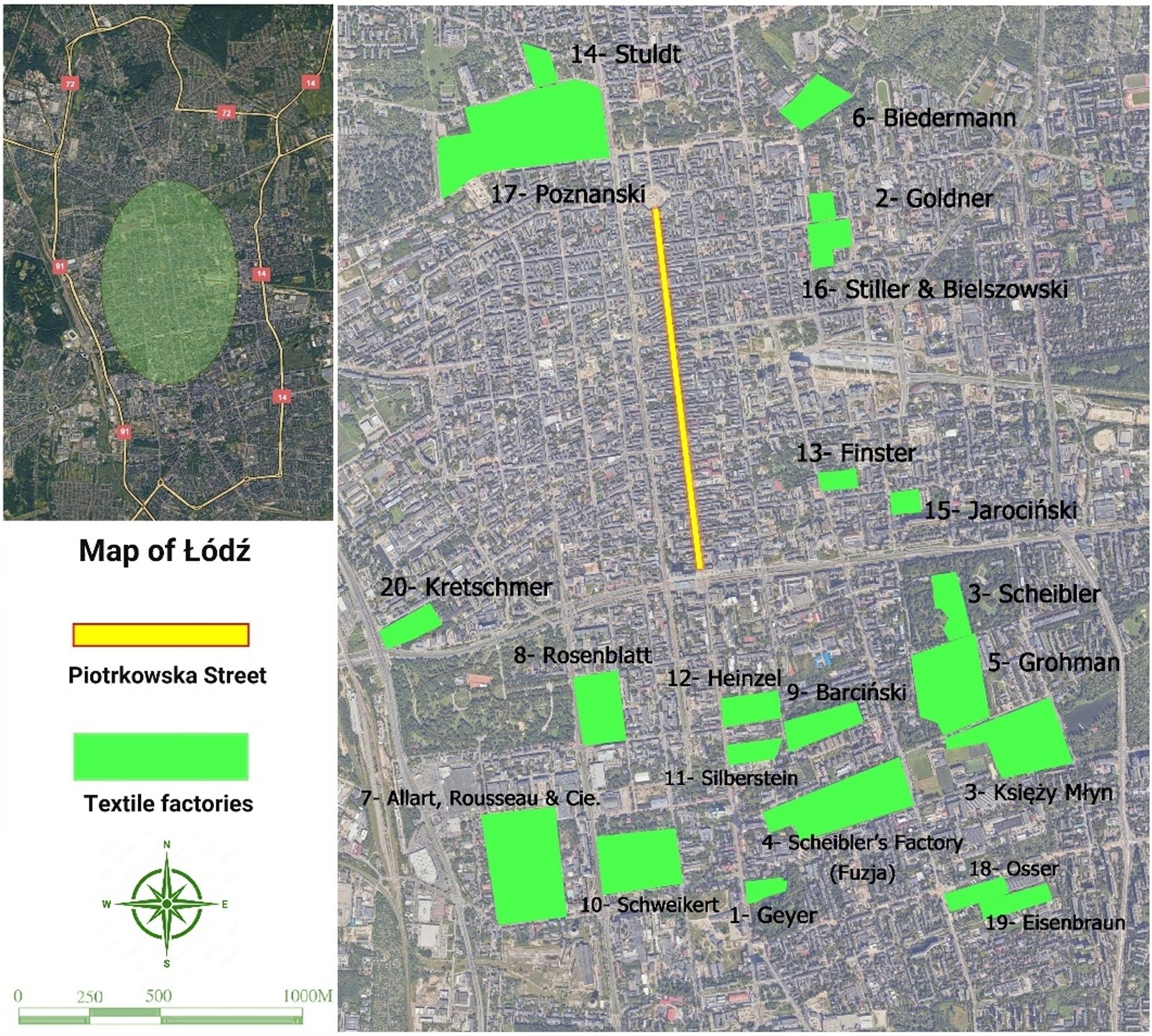
Exploring the Effectiveness of Urban Regeneration: The Comparative Study of the Industrial Heritage Sites of Łódź (Poland) and Yazd (Iran)
Published 2025-09-08
Keywords
- Effective urban regeneration,
- industrial heritage,
- sustainability,
- revitalization,
- Poland
- Iran,
- adaptive reuse ...More
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohammadhossein Dehghan Pour Farashah, Zdzisława Elżbieta Niemczewska, Pedro Porfírio Coutinho Guimarães

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2025-09-06
Published 2025-09-08
Abstract
To establish appropriate strategies for the urban regeneration of districts with industrial heritage, it is essential to consider the factors that may influence the effectiveness of any regeneration. This study compares the revitalisation of industrial heritage sites in Łódź, Poland, as a European regeneration model, and Yazd, Iran, as an Asian counterpart—two cities that share similar textile manufacturing histories but possess distinct political, cultural, and socio-economic factors. The study examines the challenges associated with achieving effective urban regeneration in the setting of industrial heritage sites. The study employed semi-structured interviews with experts and professionals, complemented by fieldwork and observational analyses of textile manufacturing heritage sites, with a particular emphasis on revitalisation projects. The originality of this paper lies in the application of a synthetic approach to the analysis of qualitative data for comparing typologies of urban regeneration strategies within the contexts of two socio-culturally and economically distinct countries. The results indicate that for effective urban regeneration within industrial heritage sites it necessitates the attainment of socio-economic outcomes through a balanced approach to public-private financing, while mitigating the undue influence of private investments. Furthermore, projects that enhance accessibility and infrastructure, as well as promote the adaptive reuse of historical resources, should be prioritised. Such initiatives not only generate financial income but also yield social benefits and contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage values. The paper provides valuable insights for urban planners regarding the effectiveness of urban regeneration processes in districts characterised by industrial heritage.
Highlights:
- The revitalisation project must be designed to align with both material and non-material values.
- Shifts from private investments to collaboration highlight the industrial heritage in Łódź.
- Substantial evidence underscores the impact of religious values on urban management in Yazd.
Downloads
References
- Baumgartner, W. H. (2025). Green Gentrification in Lisbon (Portugal): A Study about Marvila’s Riverfront. European Journal of Geography, 16(2), 108-121. https://doi.org/10.48088/ejg.w.bau.16.2.108.121
- Bullen, P. A., & Love, P. E. D. (2011). Adaptive reuse of heritage buildings. Structural Survey, 29(5), 411-421. https://doi.org/10.1108/02630801111182439
- Chondrogianni, D., & Stephanedes, Y. (2022). Visiting Index: Supporting decision-making on Open Urban Spaces. European Journal of Geography, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.48088/ejg.d.cho.12.1.037.050
- Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2018). Using thematic analysis in counselling and psychotherapy research: A critical reflection. Counselling and Psycho-therapy Research, 18(2), 107-110. https://doi.org/10.1002/capr.12165
- Cysek-Pawlak, M., Krzysztofik, S., & Makowski, A. (2023). Urban regeneration and urban resilience planning through connectivity: the im-portance of this principle of new urbanism. European Spatial Research and Policy, 29(1), 111-133. https://doi.org/10.18778/1231-1952.29.1.06
- Dehghan Pour Farashah, M. (2023). Evaluation of social and economic values in textile manufacturing heritage sites: the case of Yazd. Ge-conservacion, 24(1), 228-237. https://doi.org/10.37558/gec.v24i1.1266
- Dehghan Pour Farashah, M., Aslani, E., & Hosseini, M. (2019). Strategic planning of industrial heritage conservation in yazd with tourism ap-proach (case study: textile factories). Proceedings of the International Conference on Conservation of 20th Century Heritage from Architec-ture to Landscape, Tehran, Iran, Tehran.
- Dehghan Pour Farashah, M., & Pourzakarya, M. (2025). Reviving the Past: Unveiling Urban Industrial Heritage in Yazd, Iran. In V. D. Truong & D. W. Knight (Eds.), Heritage Tourism: Vietnam and Asia (pp. 165-186). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-5427-7_9
- Dell’Anna, F. (2022). What Advantages Do Adaptive Industrial Heritage Reuse Processes Provide? An Econometric Model for Estimating the Impact on the Surrounding Residential Housing Market. Heritage, 5(3), 1572-1592. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030082
- Della Lucia, M., & Pashkevich, A. (2023). A sustainable afterlife for post-industrial sites: balancing conservation, regeneration and heritage tour-ism. European Planning Studies, 31(3), 641-661. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2022.2154141
- El-Basha, M. S. (2021). Urban interventions in historic districts as an approach to upgrade the local communities. HBRC Journal, 17(1), 329-364. https://doi.org/10.1080/16874048.2021.1938892
- Esfahani, H. S., & Pesaran, M. H. (2009). The Iranian economy in the twentieth century: A global perspective. Iranian Studies, 42(2), 177-211. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25597543
- Ferilli, G., Luigi, S. P., Giorgio, T. B., & Forbici, S. (2017). Power to the people: when culture works as a social catalyst in urban regeneration pro-cesses (and when it does not). European Planning Studies, 25(2), 241-258. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2016.1259397
- Galuszka, J. (2022). Beyond the decay? Positive patterns in the development of a large housing estate: the case of Olechów-Janów district in Łódź, Poland. Urban Research & Practice, 15(2), 169-193. https://doi.org/10.1080/17535069.2020.1782459
- Ghaderi, Z., Aslani, E., Beal, L., Dehghan Pour Farashah, M., & Ghasemi, M. (2024). Crisis-resilience of small-scale tourism businesses in the pan-demic era: the case of Yazd World Heritage Site, Iran. Tourism Recreation Research, 49(5), 1197-1203. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2022.2119519
- Ghaderi, Z., Dehghan Pour Farashah, M. H., Aslani, E., & Hemati, B. (2020). Managers’ perceptions of the adaptive reuse of heritage buildings as boutique hotels: insights from Iran. Journal of Heritage Tourism, 15(6), 696-708. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743873X.2020.1756834
- Guimarães, P. P. C. (2017). An evaluation of urban regeneration: the effectiveness of a retail-led project in Lisbon. Urban Research & Practice, 10(3), 350-366. https://doi.org/10.1080/17535069.2016.1224375
- Guo, P., Li, Q., Guo, H., & Li, H. (2021). Quantifying the core driving force for the sustainable redevelopment of industrial heritage: implications for urban renewal. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(35), 48097-48111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14054-7
- Huang, L., Zheng, W., Hong, J., Liu, Y., & Liu, G. (2020). Paths and strategies for sustainable urban renewal at the neighbourhood level: A frame-work for decision-making. Sustainable Cities and Society, 55, 102074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102074
- Hulsbergen, E., Klaasen, I. T., & Kriens, I. (2005). Shifting Sense: Looking back to the future in Spatial Planning. Techne Press Amsterdam.
- Hwang, K. H. (2014). Finding Urban Identity through Culture-led Urban Regeneration. Journal of Urban Management, 3(1), 67-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2226-5856(18)30084-0
- ICOMOS, A. (2013). The Burra Charter: The Australia ICOMOS charter for places of cultural significance. Australia ICOMOS Incorporated. https://doi.org/https://australia.icomos.org/publications/burra-charter-practice-notes/
- Jarczewski, W., & Koj, J. (2023). Spatial factors affecting the functional diversity of regenerated brownfields: The case of Silesian Voivodeship (Poland). Moravian Geographical Reports, 31(2), 84-94. https://doi.org/10.2478/mgr-2023-0008
- Kazimierczak, J., & Kosmowski, P. (2018). Post-industrial urban areas in the context of ruination, demolition and urban regeneration in a post-socialist city: Experiences of Łódź, Poland. Finisterra, 53(109), 35-51. https://doi.org/10.18055/Finis12092
- Konior, A., & Pokojska, W. (2020). Management of Postindustrial Heritage in Urban Revitalisation Processes. Sustainability, 12(12).
- Kuzior, A., Grebski, W., Kwilinski, A., Krawczyk, D., & Grebski, M. E. (2022). Revitalisation of Post-Industrial Facilities in Economic and Socio-Cultural Perspectives—A Comparative Study between Poland and the USA. Sustainability, 14(17).
- Liu, Y., Shen, L., Ren, Y., & Zhou, T. (2023). Regeneration towards suitability: A decision-making framework for determining urban regeneration mode and strategies. Habitat International, 138, 102870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2023.102870
- Maghsoodi Tilaki, M. J., & Farhad, S. (2024). A qualitative investigation of revitalisation efforts to foster residents’ attachment in dilapidated neighbourhoods: Is identity a matter? Journal of Urban Management, 13(4), 639-656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jum.2024.07.003
- Martinović, A., & Ifko, S. (2018). Industrial heritage as a catalyst for urban regeneration in post-conflict cities Case study: Mostar, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Cities, 74, 259-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2017.12.013
- Mokras-Grabowska, J., & Mroczek-Żulicka, A. (2024). Creative use of post-industrial space in Lodz - tour guides’ perspectives. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change, 22(4), 438-455. https://doi.org/10.1080/14766825.2024.2402853
- Nocca, F., Bosone, M., & Orabona, M. (2024). Multicriteria Evaluation Framework for Industrial Heritage Adaptive Reuse: The Role of the ‘Intrin-sic Value’. Land, 13(8).
- Pendlebury, J. (2008). Conservation in the Age of Consensus. Routledge.
- Ploegmakers, H., & Beckers, P. (2014). Evaluating urban regeneration: An assessment of the effectiveness of physical regeneration initiatives on run-down industrial sites in the Netherlands. Urban Studies, 52(12), 2151-2169. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098014542134
- Pollard, J. S. (2004). From Industrial District to 'Urban Village'? Manufacturing, Money and Consumption in Birmingham's Jewellery Quarter. Urban Studies, 41(1), 173-193. https://doi.org/10.1080/0042098032000155731
- Pulles, K., Conti, I. A. M., Kleijn, M. B. d., Kusters, B., Rous, T., Havinga, L. C., & Ikiz Kaya, D. (2023). Emerging strategies for regeneration of historic urban sites: A systematic literature review. City, Culture and Society, 35, 100539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccs.2023.100539
- Ramazankhani, M. R. (2016). Regeneration of Industrial Heritage with Emphasis on Maintaining Cultural Values, Case Study: Spinning and Wrapping Factory of Nasadjan Yazd. University of Tehran. Tehran. https://ut.ac.ir/fa/thesis/19617/
- Ren, Y., Li, H., Shen, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., & Wang, J. (2018). What Is the Efficiency of Fast Urbanization? A China Study. Sustainability, 10(9).
- Roberts, P. (2000). The Evolution, Definition and Purpose of Urban Regeneration. In P. Roberts & H. Sykes (Eds.), Urban Regeneration A Hand-book (pp. 9-36). Sage.
- Samadzadehyazdi, S., Ansari, M., Mahdavinejad, M., & Bemaninan, M. (2020). Significance of authenticity: Learning from best practice of adap-tive reuse in the industrial heritage of Iran. International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 14(3), 329-344. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2018.1542466
- Szmygin, B. (2009). Adaptacja obiektów zabytkowych do współczesnych funkcji użytkowych. Lubrlskie Towarzystwo Naukowe : Międzynarodowa Rada Ochrony Zabytków ICOMOS ; Politechnika Lubelska.
- Szymański, T. (2017). Cultural Identity of the Industrial Heritage in Gdansk. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 245(8), 082034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/245/8/082034
- Tang, J., Zhu, H.-l., Liu, Z., Jia, F., & Zheng, X.-x. (2019). Urban Sustainability Evaluation under the Modified TOPSIS Based on Grey Relational Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(2).
- UNESCO. (2025). Historic city of Yazd. Retrieved 29/06/2023 from https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1544/
- Vafaie, F., Remøy, H., & Gruis, V. (2023). Adaptive reuse of heritage buildings; a systematic literature review of success factors. Habitat Interna-tional, 142, 102926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2023.102926
- van Duijn, M., Rouwendal, J., & Boersema, R. (2016). Redevelopment of industrial heritage: Insights into external effects on house prices. Re-gional Science and Urban Economics, 57, 91-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2016.02.001
- Vardopoulos, I. (2023). Adaptive Reuse for Sustainable Development and Land Use: A Multivariate Linear Regression Analysis Estimating Key Determinants of Public Perceptions. Heritage, 6(2), 809-828.
- Venice Charter. (1964). ICOMOS. International Council on Monuments and Sites. https://doi.org/https://www.icomos.org/charters-and-doctrinal-texts/
- Walczak, B. (2015). The Image of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Łódź. Envisioning Architecture: Image, Perception and Communication of Herit-age, 17-26.
- Walczak, B. M., & Kępczyńska-Walczak, A. (2024). Adaptive Re-use of Industrial Heritage in Lodz, Poland. International Journal of Conservation Science, 15(2), 955-966. https://doi.org/10.36868/IJCS.2024.02.13
- Wilkinson, S. J., Remøy, H., & Langston, C. (2014). Sustainable building adaptation: innovations in decision-making. John Wiley & Sons.
- Wrona, A. (2020). Gentrification as part of urban development. Biblioteka Regionalisty(20), 194-202.
- Yin, J., & Feng, J. (2024). Research on the design of narrative space construction: a case study of the revitalisation project of the Macau Lychee Bowl Shipyard. Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/13467581.2024.2390615
- Zhang, X., & Ren, Y. (2024). Revitalisation of urban industrial heritage from a perspective of spatial production theory: the case study of “Old market” project. Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13467581.2024.2396618
- Zhang, Y., Kang, S., & Koo, J.-H. (2019). What Is the Critical Factor and Relationship of Urban Regeneration in a Historic District?: A Case of the Nanluoguxiang Area in Beijing, China. Sustainability, 11(23).
- Zhao, P., Md Ali, Z., & Ahmad, Y. (2023). Developing indicators for sustainable urban regeneration in historic urban areas: Delphi method and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Sustainable Cities and Society, 99, 104990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104990
- Zheng, H. W., Shen, G. Q. P., Song, Y., Sun, B., & Hong, J. (2016). Neighborhood sustainability in urban renewal: An assessment framework. Envi-ronment and Planning B, 44(5), 903-924. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265813516655547




